What is Asthma?
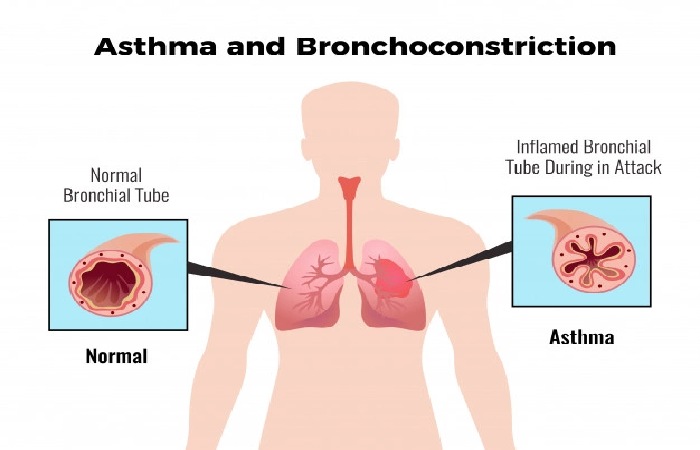
In asthmatics, Asthma causes the bronchial tubes react overly sensitively due to chronic inflammation. The bronchi are a widely branched system of pipes that direct the breathing air from the trachea to the tiny air sacs in the lungs, where gas exchange occurs – oxygen is engrossed into the blood and carbon dioxide is released into the exhaled air.
In asthma, the mucous membrane lining the inside of the bronchi swells and produces thick mucus.
As a result, the inner width of the bronchi narrows and the patient finds it more difficult to breathe in and out. Accordingly, he lives faster – the respiratory rate increases.
I was exhaling, in particular, works worse. It can sometimes hear n whistling or rumbling breath sounds. In severe cases, some air remains in the lungs with every breath, leading to hyperinflation.
The gas exchange then only works to a limited extent so that a lack of oxygen in the blood can develop.
Asthma occurs in flares. This means that the indications recover repeatedly or disappear entirely in between.
The reasons for asthma are not fully understood. Asthma causes Several factors at play likely cause the bronchi to become hypersensitive (hyperresponsivity) to various stimuli and cause them to over constrict – as described above. As mentioned above, doctors differentiate between asthma due to an underlying allergy and asthma that occurs without an allergy. Most children with asthma have underlying allergic reactions, less common in adults.
A unique feature is narrowing the airways due to (accumulated) viral infections of the lungs in small children (obstructive bronchitis ). This can lead to asthma-like symptoms, which disappear again with increasing age. Therefore, this is not asthma.
Because the prevalence of asthma varies significantly worldwide, diet, hygiene and other living conditions are likely to play a role. In addition, the family predisposition plays an important role:
If the father and mother have asthma, the risk for the offspring is significantly increased to also suffer from this chronic lung disease. There is also a link between asthma and other allergies. The risk of developing (allergic) asthma is more remarkable if people or close relatives have allergic diseases (such as hay fever or neurodermatitis ) or suffer from them in childhood.
Risk Of Smoking
Smoking during pregnancy and passive smoking in childhood also increases the risk.
In addition, indoor climate (house dust, mould formation), air pollution (exhaust gases) and irritating substances in the workplace (e.g. chemicals, dust, allergens) can also contribute to a person developing asthma and the symptoms worsening.
According to some studies, children are more likely to develop asthma when exposed to paracetamol or very broad-spectrum antibiotics during pregnancy or early childhood. However, the study results are unclear, only representing a possible connection.
Nevertheless, pregnant women should only take paracetamol or antibiotics or give them to their babies if necessary. If in doubt, however, seek medical advice because antibiotics, in particular, can also be life-saving.
In addition, overweight children have asthma more frequently than children of average weight; asthma therapy often does not work that well.
The environment around farms offers protection against the development of bronchial asthma if the child has had a lot of contact with various germs (especially from the cowshed) and has drunk fresh cow’s milk during early childhood.
The impact of respiratory viral infections in childhood is unclear: such diseases may contribute to or possibly protect against asthma.
Anyone who already suffers from an allergy should not have cats or other small animals in the house. However, early contact with pets in families with no known allergy/asthma appears to protect against the development of asthma.
Overall, however, the studies on whether pet ownership tends to trigger or protect against asthma are often contradictory, so this question has not yet been clarified.
What Triggers an Asthma attack?
Many substances can trigger an asthma attack. If there is an allergy, the affected persons react, e.g. B. on contact with house dust mites, animal hair from dogs or cats or pollen with breathing difficulties and coughing. Occupational asthma can develop in people who contact animals, fish products and flour, building materials, certain gases and chemicals.
Tiny particles of these substances enter the lungs when inhaled or through the blood. These substances irritate the mucous membrane in the airways, causing them to swell and the bronchi to constrict. It makes exhalation more difficult and leads to coughing.
Even people who do not suffer from allergies can react to certain irritants or triggering factors with asthmatic symptoms (e.g. tobacco smoke, car exhaust fumes, cold air, strong perfume, etc.).
Infections of the respiratory tract often cause asthmatic symptoms. Some people with asthma have trouble breathing after exercising ( exercise asthma ).
A seizure can be triggered by several factors in some patients, while others only react to a specific substance or trigger. In addition, dissimilar people may respond differently to the same triggering factor.
Certain medications, including some blood thinners and pain relievers such as acetylsalicylic acid and NSAIDs, can trigger severe asthma attacks in some people. In addition, some heart medications (beta-blockers) can also trigger or worsen asthma.
In addition, severe emotional stress ( anxiety ) can lead to coughing and shortness of breath in those affected.
Over time, many people who have asthma become aware of the factors that cause the symptoms and avoid them.